Flagellar membrane transport events are discriminated from nonspecific cell movement by the following selection criteria. Cell Membrane and Transport.

Cell Transport Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
There must not be an appreciable difference in the level of the baseline before and after a transport event.
. Passive Transport by Facilitated Diffusion. Remove a section of tubing from the distilled water and separate the sides to form a tube. One of the functions of membranes is to control what passes into and out of the cell.
B In pinocytosis the cell takes in small particles in fluid. The shape change exposes the molecule to the other side and it is transported. Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article.
Passive transport is the movement of substances across the membrane without the expenditure of cellular energy. Passive and Active Transport 1. There must not be appreciable movement of either the flagellum or the cell body.
Ion transport membranes ITM are nonporous multicomponent oxides suited to work at temperatures above 973 K and have high oxygen flux and selectivity Dyer Richards Russek Taylor 2000. 262 Ion transport membrane reforming. 2 days agoThe chitosan membrane soaked in water has a low tensile strength 05 MPa which prevents its use as a robust ion exchange membrane.
Both form continuous proteinpathways across the lipid bilayer. The transmission of chemical information across lipid bilayer membranes is crucial in biological. Students identify structures within the bilayer and use reasoning to determine how molecules are moving across the membrane in response to a hypertonic solution.
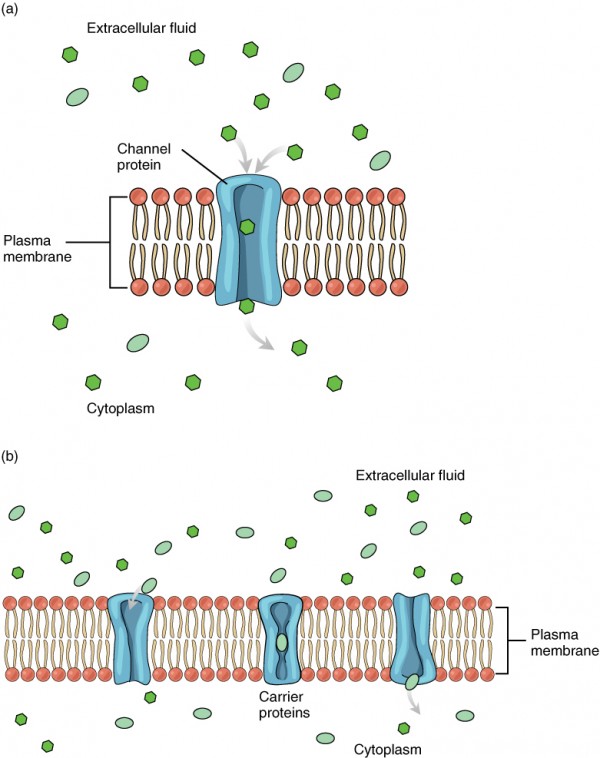
Carrier Proteins change shape when they bind to a molecule. Click Here for a more elaborate picture of a cell membrane. Water moves in the direction necessary to equalize the concentrations.
Term used for the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. The transport across cell membrane is classified into three types. Passive vs Active Processes.
In cellular biology membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them. The transport of most ions occur more slowly than the non- electrolytes. The initial design was carried out for a hydrogen refuelling station dispensing about 12000 Nm 3 H 2 day.
There are two classes of membrane transport proteinscarriers and channels. Phospholipids arranged in a bilayer and membrane proteins. Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways.
Transport across a cell membrane questions. In active transport ATP is required to pump substances against a concentration. Controlled membrane translocation provides a mechanism for signal transduction and amplification.
This is the currently selected item. The red cell is easily penetrated by Cl and HCO 3. Processes that move substances across membranes can be grouped into two general categories based on whether the process requires an input of cellular energy or not.
This reinforcement worksheet displays a graphic of the cell membrane showing the phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins. A In phagocytosis which is relatively nonselective the cell takes in a large particle. In passive transport substances move passively they diffuse.
In both processes solutes move through transport proteins in the cell membrane. Active transport requires energy in the form of ATP solute from lower concentration to higher concentration transport through cell membrane. Molecule is shielded from the lipid bilayer and molecule is released and protein goes back to normal shape.
Cell Membrane and Transport Review. Terms in this set 40 A Solution that contains low solute and high solvent compared to another solution. Passive Transport Passive processes do not use ATP but do need some sort of driving force.
CSqueeze the air out of the bag and place a. The structure of the cell membrane is designed so that it does not allow free movement of substances. In contrast active transport is the movement of substances across the membrane using energy from adenosine triphosphate ATP.
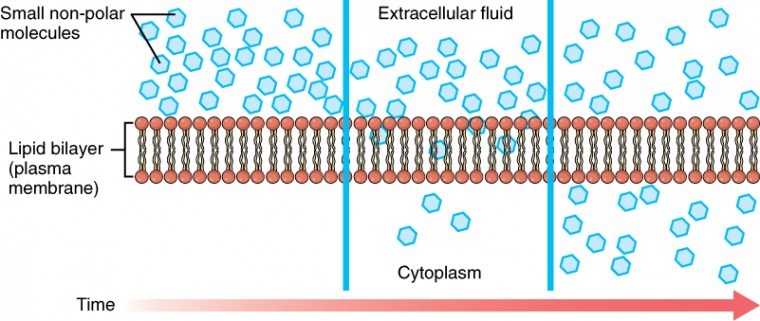
If no energy input is required for the transport then we say particles move via a passive transport process. Recall that membranes have two major components. How do things move across a cell membrane.
The membrane itself contains polar groups and is therefore electrically charged. Endocytosis is a form of active transport in which a cell envelopes extracellular materials using its cell membrane. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most but not all molecules.
C In contrast receptor-mediated endocytosis is quite selective. If the transport of molecules across the membrane is mediated by a transmembrane protein but the force driving transport is either a concentration gradient chemical force or an electrochemical gradient the process is facilitated diffusion. The regulation of passage through the membrane is due to selective membrane permeability - a characteristic of biological.
Whereas transport by carriers can be either active or passive solute flow through channel proteins is always passive. This passage of molecules is a type of passive transport and no energy is required because molecules are still moving according to the concentration gradient. A resting non-signaling neuron has a voltage across its membrane called the resting membrane potential or simply the resting potential.
But H OH penetrate all cell membranes easily. Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment. Admin October 8 2017.
Types of transport across cell membrane are listed below. In this module you will review mechanisms of membrane transport. To allow ions in and out of the cell many places along the cell membrane contain channels which let ions across the membrane in a process known as facilitated diffusion.
The cell membrane transport occurs in two major ways like. Place a plastic clip across the bottom of the tubing. The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and.
Diffusion Passive Transport 2. Bulk transport phagocytosis and pinocytosis Cell Membrane Transport. Fill each bag with about 10 ml of solution using a 10 ml graduated pipette.

Membrane Transport Anatomy And Physiology

0 Comments